Immunomics Services
Immunomics Services for Mast Cells
Mast cells are innate immune cells involved in immune surveillance and defense. They are known for releasing and producing mediators of allergic reactions. CD Genomics offers immunomics services for mast cells to help you explore their characteristics in terms of development, recruitment, heterogeneity, and responsiveness.
Introduction to Mast Cells
Mast cells belong to a lineage of hematopoietic cells that originate from the pluripotent progenitor cells of the bone marrow and are present in connective tissue throughout the body and do not circulate in the blood. The activation and degranulation of mast cells have a marked regulatory effect on many aspects of physiological and pathological conditions in a variety of situations. In order for mast cells to migrate to their target location, the coordinated action of integrins, adhesion molecules, chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors is required.
Physiological Roles of Mast Cells
Mast cells are responsible for regulating various physiological functions, including vasodilation, angiogenesis, and the elimination of bacteria and parasites. In addition, mast cells regulate the functions of many cell types such as dendritic cells, macrophages, T cells, B cells, fibroblasts, eosinophils, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells. Because mast cells produce and release pluripotent molecules such as histamine, proteases, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, heparin, and many cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, they have the capacity to be involved in regulating the function of many organs and tissues.
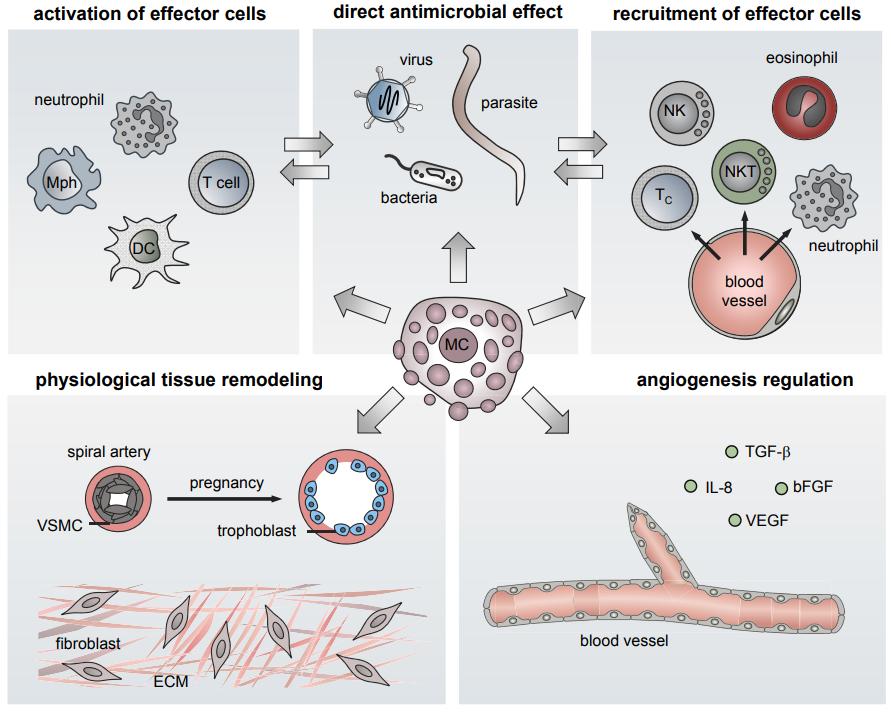 Fig.1 The role of mast cells. (Dudeck, A., et al., 2019)
Fig.1 The role of mast cells. (Dudeck, A., et al., 2019)
Immunomics Studies for Mast Cells
Mast cells are found in the mucous membranes and epithelial tissues throughout the human body. Mast cells are innate immune cells characterized by their inflammatory mediator granules and are primarily known for their role in allergic responses.
Immunomics studies of mast cells facilitate a deep understanding of their important role in the disease process. Mast cells are scattered in the interstitial of tumors and there is evidence of their promotional and anti-tumor effects. A multi-omics database study has shown that mast cell fraction facilitates effective prediction and warning of cancer metastatic potential.
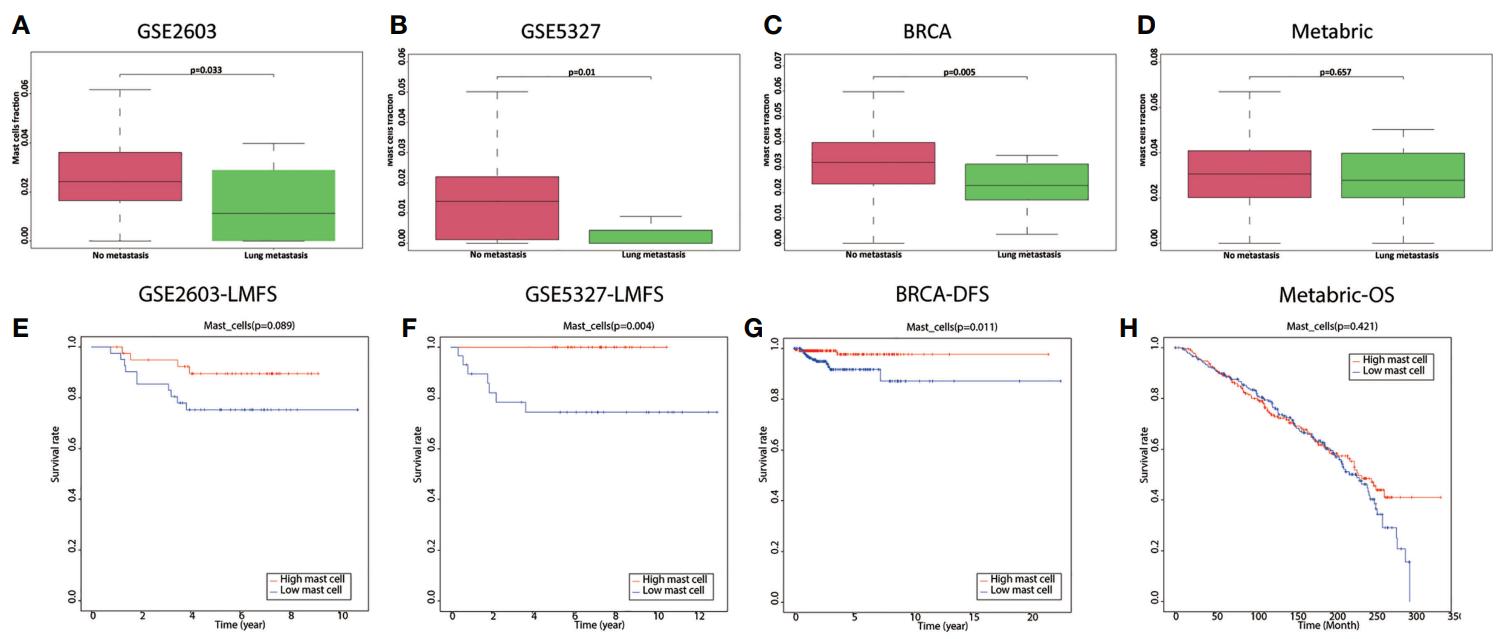 Fig.2 Multiple experimental cohorts demonstrate that the distribution of mast cells is associated with lung metastatic status. (Zhang, L., et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Multiple experimental cohorts demonstrate that the distribution of mast cells is associated with lung metastatic status. (Zhang, L., et al., 2022)
Our Services
Mast cells are immune cells found in almost all tissues, but their excessive activity and pathological state can lead to many health hazards. The role of mast cells is still poorly understood, making it difficult to develop treatments for their pathological state. CD Genomics offers several types of immunomics services to help clients understand the mechanisms of mast cells in the immune process.
In addition, we have a professional data analysis team to help clients process and interpret experimental data in depth in order to understand the data of multiple characteristics of mast cells under different conditions.
Why Choose Us
Based on a wide range of omics research platforms, CD Genomics provides clients with reliable immunomics analysis of mast cells. We help our clients to build experimental solutions, conduct experiments, and analyze experimental data through in-depth communication and collaboration with them. Please contact us for more information.
References
- Dudeck, A., Köberle, M., Goldmann, O., Meyer, N., Dudeck, J., Lemmens, S., ... & Biedermann, T. (2019). Mast cells as protectors of health. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology, 144(4), S4-S18.
- Zhang, L., Pan, J., Wang, Z., Yang, C., Chen, W., Jiang, J., Zheng, Z., Jia, F., Zhang, Y., Jiang, J., Su, K., Ren, G., & Huang, J. (2022). Multi-Omics Profiling Suggesting Intratumoral Mast Cells as Predictive Index of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis. Frontiers in oncology, 11, 788778.
